Food Chain In The Ocean Biome
Seals, walruses, sea lions, and dolphins are common examples of such sea animals.
Food chain in the ocean biome. A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (figure 8.3). On the ocean's surface waters, microscopic animals—zooplankton, which include jellyfish. This is evident in the diagram complementing this article.
For an environment to remain healthy, the food chain must remain unbroken. Some of the plants in this first level of food chain are phytoplankton, seaweed, sea grass, and many other plants. Marine biome is primarily found in five oceans like the pacific, the atlantic, the arctic, the indian, and the southern oceans.
3 different food chains. Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly. Food web is a connection of multiple food chains.
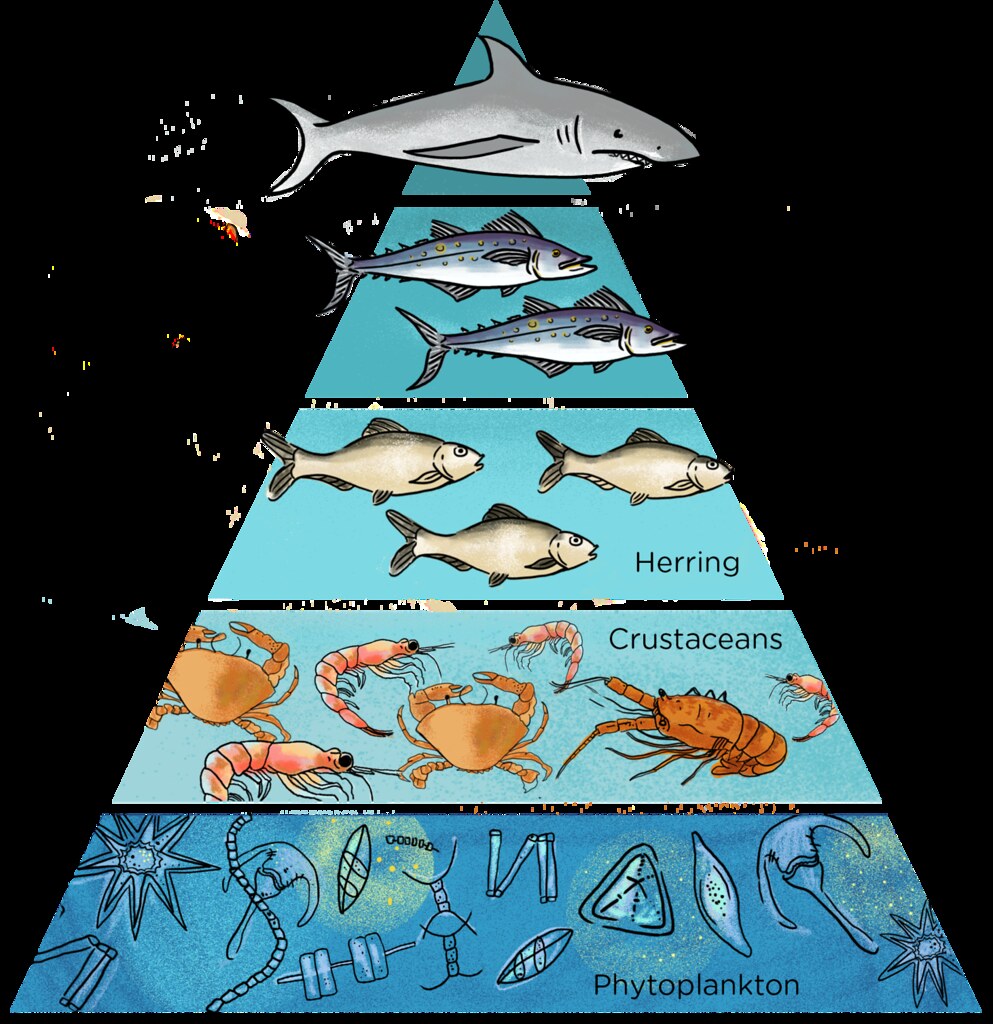
Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. Covering 71 percent of the earth’s surface, the ocean provides a magnificent variety of creatures. For natural reasons, the ocean biome is colder near the poles, but near the equator, it becomes warmer as the sun strikes the water directly, with a.
A food chain is a single pathway connecting a producer with several levels of consumers. These organisms are called the producers, and they get their energy directly from sunlight and inorganic nutrients. Summarize that microbes, including phytoplankton and bacteria, are the beginning and end, respectively, of ocean food chains and are therefore essential components of marine ecosystems.
Food chains are usually in a sequence, with an arrow used to show the flow of energy. The most productive producers in the ocean are phytoplankton. In the ocean, a food chain typically starts with energy from the sun powering phytoplankton, and follows a course such as:



















